Introduction
Selecting an appropriate lease structure for a commercial property can seem daunting. Commercial real estate contracts can be structured in a variety of ways. The triple net lease (NNN) structure tops all other lease contracts. The NNN lease is used in commercial real estate’s retail, industrial, and office sectors. Investors and landlords commonly use the NNN lease because it provides a stable and predictable income stream, as the tenant is responsible for paying most of the operating expenses. The NNN lease is also attractive to tenants because it offers greater control over the property and allows the tenant to budget for operating expenses in advance. This article, by Allies Commercial Realty, will cover the basics of the triple net lease, its functions, and its advantages & disadvantages relative to other commercial lease structures.
Triple Net Lease (NNN)
A business may need a shorter or longer term lease, depending on where they are with their business cycle. For instance, when a company grows, it may need more flexibility to make room for more personnel and divisions, or it may need to install new technology for its use. A triple-net lease, also known as a “NNN lease,” is a commercial real estate lease type in which the tenant pays their pro-rata share of operating expenses associated with the property, along with the base rent. These operating expenses may include property taxes, insurance, and common area maintenance (CAM). In an NNN lease, each N refers to “Net,” and the term “Net” stands for each form of net expense paid by the Tenant (i.e., property taxes, insurance, and CAM). Commercial lease contracts typically range from three (3) to five (5) years, sometimes even longer.
Commercial Real Estate Lease Types
Three common lease structures are used in commercial real estate lease contracts. Landlords can choose the appropriate lease type for their specific property. The three common lease structures are as follows
- Full-Service Lease
- Triple Net Lease
- Modified Gross Lease
Full-Service Lease: In a full-service lease, tenants are responsible for making one payment, including the base rent, and their pro-rata share of operating expenses, including janitorial and utilities. Tenants see the amount they will pay monthly when they sign a full-service lease agreement. This lease structure prevents cost fluctuation caused by maintenance, usage, and other issues.
Triple Net Lease: The base rent for this type of lease is relatively lower than the full-service lease. However, the tenant still has to pay their pro-rata share of property taxes, insurance, common area maintenance (CAM), etc. Pro-rata (Latin term that means “in proportion.”) in this context refers to the proportionate share of common expenses (property taxes, insurance, maintenance, etc.) that each tenant of a property is responsible for paying. Landlords can often pass through additional operating expenses such as management and administrative fees. Net leases can be classified into four categories:
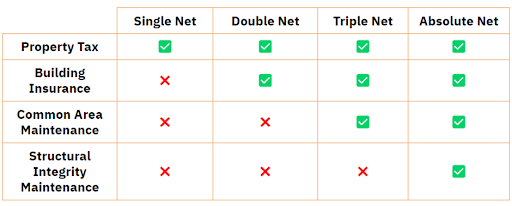
Single Net Lease: Also known as N Lease, tenants pay the base rent and their pro-rata share of property taxes.
Double Net Lease: In addition to base rent, tenants are responsible for their pro-rata share of property taxes and building insurance. A double-net lease is also known as a NN lease.
Triple Net Lease: A net lease, or NNN lease, is a lease agreement where tenants pay for base rent, their pro-rata share of property taxes, building insurance, and CAM.
Absolute net lease: the Tenant bears all expenses, including structural maintenance. In this kind of lease structure, the landlord has no responsibility.
Fig: Comparison between different forms of net leases
Modified Gross Lease: A modified gross lease is the combination of gross and net leases. The landlord and tenant each bear a portion of the risk in this lease. Modified gross leases are more common in multi-tenant buildings but are starting to become obsolete.
How To Calculate Triple Net Lease
A triple net lease can be calculated in several ways. We can simplify the formula as follows:
NNN Lease = Base Rent + Property Tax + Insurance + CAM
One way is to add the annual base rent to the pro-rata share of property taxes, insurance, and common area maintenance expenses and divide the total by 12. This will equate to the monthly payment for the lease. The base rent is calculated based on a rate per square foot. The process is simple when only one tenant is leasing the property. But when there are multiple tenants, property taxes, insurance, and common area maintenance expenses are fragmented according to the Tenant’s rental square footage. Let’s look at an example to understand better how triple-net lease functions.
Example:
Think of a commercial real estate listing where 25,000 SF is rented to a trucking company. The landlord and the tenant have agreed upon a triple-net lease agreement. The annual base rent per square foot is $8.25. The annual property tax for the property is $600, the yearly insurance payable is $1,400, and the common area maintenance charge is $1,240. We need to calculate the total lease rate per month for this company.
Calculation:
To begin, we must determine the base rent: Base Rent is calculated by multiplying the price per square foot rent by the total rental square footage.
Annual Base Rent= 8.25 x 25,000 = $206,250
To find the total annual lease amount, we need to add all the annual expenses to the yearly base rent amount.
Annual Lease amount = Base Rent + Tax + Insurance + CAM
Annual Lease amount = $206,250 + $600 + $1,400 + $1,240 = $209,490
To determine the lease rate per month, the total annual lease amount needs to be divided by 12.
Total Monthly Lease Rate = Total Annual Lease amount / 12
Total Monthly Lease Rate = $209,490 / 12 = $17,457.50
So, the total lease amount per month is $17,457.50, which the trucking company needs to pay the landlord.
Why Do You Want a Triple Net Lease?
There are many advantages to triple-net leases for both landlords and tenants. Among the benefits, it is a transparent way for both landlords and tenants to keep track of the operating expenses for the property. It also allows a landlord to collect rental income without having many active responsibilities. We have discussed the pros and cons below:
Pros:
– Triple-net leases are generally binding, meaning the tenant cannot back out before the expiration date. Unless the tenant’s business goes bankrupt, the risk is relatively low in this commercial real estate investment.
– Most triple net leases are long-term, typically lasting for three to five years, and include annual rent escalations.
– Triple net leases are popular among tenants because there is transparency for the operating expenses for which they are responsible. They can see precisely what the landlord charges for real estate taxes, insurance, CAM, management & administrative fees, etc. And landlords provide an opportunity to maintain a passive role and benefit from a steady cash flow with relatively low risk.
Cons:
– Triple net leases require the tenant to pay for all additional expenses, including maintenance and repairs, rent, property taxes, and insurance premiums. The tenant is also responsible for paying utilities, such as electricity, gas, and water, unless these costs are included in the base rent. Rent cannot be altered for any reason, including unexpected increases in ancillary expenses.
– Landlords locked into a long-term lease lose the ability to increase the rent if property values in the area increase, which can limit earning potential in the long term. Tenants who agree to a triple net lease become responsible for all associated liabilities, including fines and penalties for late or incorrect tax remittances.
– The Landlord may be responsible for the roof, structure, and sometimes the parking lot. The tenant may have to pay for uninsured damage and thus choose not to report it to avoid paying for it. This could leave the landlord with unreported expenses once the lease is up.
Conclusion
The triple net lease is advantageous to landlords and tenants since it provides them with several benefits. Landlords looking for a seamless income with relatively low risk can select an NNN lease while leasing their property for a long duration. On the contrary, tenants who want to establish their business in a place for a more extended period as they grow their business can choose a property with a NNN Lease. As a tenant, they will be assuming a significant amount of responsibility for the property. It’s flexible and can be customized in various ways, and the terms and conditions of the lease will depend on the needs and goals of the landlord and tenant. It is crucial for both parties to carefully review the agreement with a commercial real estate attorney and understand the contract before executing it. To better understand the terms and structure of the lease and to engage in a better negotiation, get in touch with our highly qualified team of commercial real estate brokers
 Apr 1, 2024
Apr 1, 2024 177 Views
177 Views
 Mar 7, 2024
Mar 7, 2024 352 Views
352 Views Jan 25, 2024
Jan 25, 2024 374 Views
374 Views Jan 2, 2024
Jan 2, 2024 293 Views
293 Views Dec 13, 2023
Dec 13, 2023 281 Views
281 Views